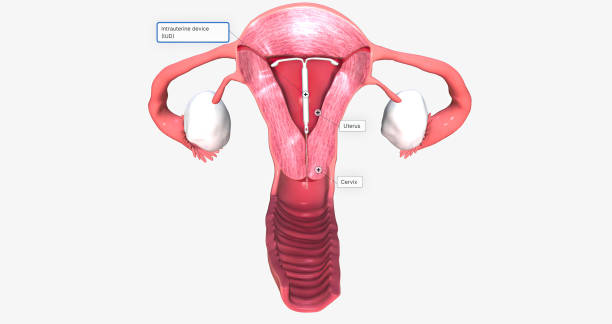
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are a popular and effective form of birth control that are implanted in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. There are two types of IUDs – hormonal and copper.
Hormonal IUDs work by releasing progestin, a hormone that thickens the cervix mucus, preventing sperm from reaching the egg. It also thins the lining of the uterus, making implantation of a fertilized egg less likely.
Copper IUDs, on the other hand, work by creating an environment that is toxic to sperm and eggs, preventing fertilization from occurring.
While IUDs are generally considered safe and effective, some women may experience side effects such as cramping, heavier periods, and mood changes. Some studies have suggested a possible link between IUD use and depression, but the evidence is not conclusive. If you are considering an IUD, talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits to determine if it’s the right option for you.
What is an IUD?
An IUD (intrauterine device) is a type of contraceptive that is inserted into a woman’s uterus to prevent pregnancy. It is a long-acting, reversible method of contraception that can be used for up to 3-10 years depending on the type of IUD used. It is one of the most effective and safe forms of birth control and does not typically cause any serious side effects.
Let’s take a closer look at how an IUD works and if it can cause depression.
Definition of an IUD
An IUD is a small, T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. The two types of IUDs are copper IUDs and hormonal IUDs.
Copper IUDs work by releasing copper ions into the uterus, which prevents fertilization and implantation of the egg. Hormonal IUDs contain a synthetic version of progesterone, which thickens cervical mucus and prevents sperm from reaching the egg. It also thins the lining of the uterus, which makes it hard for a fertilized egg to implant.
While some studies have suggested that hormonal IUDs may cause depression in some women, the link is not yet fully understood and more research is needed.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before deciding to get an IUD and to discuss any potential risks and side effects.
Types of IUD (Hormonal And Copper-Based)
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are a popular form of birth control used by many women because they are highly effective and long-lasting. There are two main types of IUDs: hormonal and copper-based.
Hormonal IUD: This type of IUD releases progestin hormone, which thickens the cervical mucus and thins the uterine lining, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. Hormonal IUDs are suitable for women who want to regulate their menstrual cycle, reduce heavy bleeding, and relieve cramps. However, hormonal IUDs can cause hormonal side effects like mood swings, weight gain, and acne.
Copper-based IUD: This type of IUD contains copper, which is toxic to sperm and prevents fertilization. Copper-based IUDs can be used for up to 10 years and do not have any hormonal side effects. However, they can cause heavy periods and cramps in some women.
It is essential to discuss the pros and cons of both types of IUDs with your healthcare provider, taking into account your medical history and specific needs. Also, while IUDs may not cause depression, they can affect mood, and it is essential to monitor any changes you experience and talk to your doctor about it.
How Does an IUD Work?
An IUD or Intrauterine Device is a small, T-shaped contraceptive device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. It works by releasing a low dose of a hormone or copper into the uterus, which thickens the cervical mucus and prevents sperm from fertilizing the egg.
There are two types of IUDs: hormonal and copper-based. Hormonal IUDs release progestin, a synthetic hormone that thickens the cervical mucus and thins the uterine lining, while copper-based IUDs release copper that creates a sperm-toxic environment in the uterus.
Some studies suggest that hormonal IUDs may increase the risk of depression and anxiety in some women. However, the overall risk is low, and many women find hormonal IUDs to be a safe and effective contraceptive choice. It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of an IUD with a healthcare provider before making a decision.
Can IUD Cause Depression
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are one of the most popular forms of contraception among women today. But when it comes to IUDs, many people are concerned about potential psychological side effects, such as depression.
While there is still a great deal of debate about whether IUDs can cause depression, there are some things that we can look at to understand more about this topic. In this article, we will discuss the possible relationship between IUDs and depression, as well as the potential risks associated with using IUDs.
Research Studies And Their Findings
There have been several research studies conducted on whether intrauterine devices (IUDs) can cause depression in women who use them as a form of birth control.
Findings from these studies have been mixed, with some suggesting a link between IUD use and increased risk of depression, while others have found no significant association.
It is important to note that individual factors, such as mental health history and lifestyle, can also contribute to the development of depression.
If you are considering using an IUD, it is essential to speak with your doctor and understand the potential risks and benefits of this form of birth control.
Pro tip: Stay informed about the latest research and consult with medical professionals to make informed decisions about your health.
The Link Between Hormonal IUDs And Depression
Research has shown that there could be a potential link between hormonal IUDs and depression in some women. While the research is inconclusive, some studies show that those who use hormonal IUDs are at a higher risk of depression than those who use non-hormonal forms of contraception.
Hormonal IUDs work by releasing small amounts of synthetic progesterone into the uterus, which can interfere with the natural hormones in the body.
If you experience symptoms of depression or mood changes while using a hormonal IUD, it’s essential to talk to your healthcare provider. Depending on your medical history, your healthcare provider may recommend switching to a non-hormonal IUD or finding an alternative form of birth control. Remember, everyone’s body is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another.
The Link Between Copper IUDs And Depression
Copper IUDs, while a highly effective contraceptive method, have been linked to an increased risk of depression in some women. This type of IUD works by releasing copper ions into the uterus, which are toxic to sperm and prevent fertilization.
Here’s how copper IUDs can cause depression:
Copper ions can interfere with the balance of minerals in the body, including zinc and magnesium, which are crucial for mood regulation and mental health.
The copper ions can also trigger an inflammatory response in the body, leading to the release of cytokines that can cause depression and other mood disorders.
It’s essential to note that not all women who use copper IUDs will experience depression, and for those who do, symptoms can vary widely in intensity and duration.
If you’re experiencing depression or any other mental health concerns while using a copper IUD, it’s essential to talk to your healthcare provider about your options for alternative contraceptives or treatment for depression.
Pro Tip: It’s crucial to communicate with your healthcare provider about any concerns or side effects you may be experiencing with your birth control method.
Benefits And Risks of IUDs
IUDs are one of the most effective forms of contraception available and are increasingly becoming a popular choice for many women. An IUD, or intrauterine device, is a small, T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
While IUDs are generally safe and effective, there are still potential risks and side effects that should be discussed when considering this method of contraception. This article will cover the benefits, risks, and potential side effects of IUDs.
The Benefits of Using an IUD
Using an intrauterine device (IUD) as a form of birth control has many benefits. IUDs are a long-lasting contraceptive option that is safe and convenient. They are more than 99% effective at preventing pregnancy, and they can last for several years without requiring replacement.
Some of the other key benefits of using an IUD include:
- Low maintenance: Once the IUD is inserted, there is no further action needed until it needs to be removed or replaced.
- Hormonal control: Some types of IUDs release hormones that can help to reduce menstrual cramps and heavy bleeding.
- Convenience: You don’t need to worry about taking a birth control pill or using condoms during sexual activity.
While IUDs have many benefits, there are also some risks to be aware of, including the potential for the device to cause depression in some women. It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about the risks and benefits of using an IUD to determine if it’s the right choice for you.
The Possible Risks of Using an IUD
The IUD is a highly effective form of birth control, but it also comes with potential risks that women should be aware of, including the risk of depression. While the connection between IUD use and depression is not fully understood, some women have reported mood changes and depressive symptoms while using an IUD.
Other possible risks of using an IUD include:
- Pain and discomfort during insertion and removal.
- Expulsion of the IUD from the uterus.
- Perforation of the uterus during insertion.
- Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy if the IUD fails.
It’s essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of using an IUD with your healthcare provider before deciding on this form of birth control. Women with a history of depression or mood disorders should be particularly cautious and vigilant for any changes in mental health while using an IUD.
Pro Tip: It’s crucial to have open communication with your healthcare provider to make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
How Effective Are IUDs?
IUDs, or intrauterine devices, are highly effective at preventing pregnancy, with a success rate of over 99%. However, they do come with both benefits and risks that should be considered before choosing to use one.
Benefits of IUDs include long-lasting contraception, which can range from 3-10 years, depending on the type of IUD used. They are also low-maintenance and do not require daily attention or ongoing prescription refills. In addition, IUDs do not contain hormones, so they do not carry the same risks of blood clots, strokes, or other hormonal side effects as other types of birth control.
Risks of IUDs can include possible expulsion or perforation of the device, as well as an increased risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), although this is rare. Additionally, some individuals may experience side effects such as cramping, irregular bleeding, or increased risk of infection. There is also some debate around whether IUDs can cause depression, but this has not been definitively proven.
Ultimately, the decision to use an IUD should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider and based on an individual’s specific health history and contraceptive needs.
IUD Insertion: What to Expect?
IUD (intrauterine device) is a form of birth control. It is a “T-shaped” device inserted in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. But how does IUD insertion work and what should you expect?
This article will cover the process of IUD insertion, what to expect during and after the procedure, and the potential risks and benefits associated with using an IUD.
Who Can Insert An Iud?
A qualified healthcare provider, such as a gynecologist, family medicine doctor, or nurse practitioner, can insert an IUD. Before the insertion, the healthcare provider will talk you through what the procedure entails, answer any questions you may have and assess if you are a good candidate for the IUD. During the insertion, you may feel some discomfort, but your healthcare provider will help you manage any pain. After the insertion, you may experience mild to moderate cramping or spotting for a few days.

IUDs are an effective form of birth control and are available in two types; hormonal or copper. Hormonal IUDs may cause side effects such as mood changes, including increased anxiety or depression. However, for most people, hormonal IUDs have been found to enhance mood and psychological health. Conversely, copper IUDs do not cause mood swings as they don’t contain hormones.
If you experience any symptoms of depression, such as persistent sadness or irritability after IUD insertion, please contact your healthcare provider for further guidance.
What Happens During An IUD Insertion?
During an IUD insertion, a healthcare provider will use a speculum to gently open the cervix, then insert a small, T-shaped device into the uterus.
Here’s what to expect in more detail:
Before the insertion, the healthcare provider will perform a pelvic exam to ensure that the uterus is in the correct position.
Next, the healthcare provider will use a speculum to gently open the vagina and visualize the cervix. They may also use a numbing medication to reduce discomfort during the procedure.
Then, the healthcare provider will use a special inserter to place the IUD into the uterus. Some people experience mild cramping or discomfort during this step.
Once the IUD is in place, the inserter is removed, leaving the IUD in the uterus. The strings attached to the IUD dangle down through the cervix and into the vagina.
After the insertion, it’s common to experience some cramping, spotting, or light bleeding for the first few days. Some people also report mood changes or other side effects, such as depression, after getting an IUD. However, research on this topic has been inconclusive so far. If you experience any concerning symptoms after getting an IUD, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider.
Possible Side Effects
While IUDs (intrauterine devices) are considered safe and effective contraceptive methods, there are possible side effects associated with their insertion and use, including depression. IUDs work by preventing fertilization, and there are two types of IUDs available – hormonal and non-hormonal.
Some of the possible side effects of IUD insertion include:
- Pain and discomfort during the insertion procedure
- Cramping and spotting after insertion
- Changes in bleeding patterns
- Perforation or expulsion of the device (rare)
- Infection
Additionally, hormonal IUDs may cause hormonal-related side effects such as mood swings, headaches, and depression. It is important to talk to your doctor if you experience any severe side effects after IUD insertion. Pro tip: It is best to get an IUD inserted by a trained medical professional to minimize the risk of complications.
IUD Removal: What to Expect?
An Intrauterine Device (IUD) is a small T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus for long-term contraception.
Removal of an IUD should be relatively easy and straightforward, but it is important to understand what to expect in order to prepare yourself for the process. In this section, we will discuss the process of IUD removal, how long it takes, and what to do afterwards.
How is an IUD Removed?
An IUD or intrauterine device is a birth control method that prevents pregnancy by inserting a small device into the uterus. When it comes to IUD removal, the process is usually straightforward and quick.
Here’s what to expect during an IUD removal: Your healthcare provider will first perform a pelvic exam and locate the strings attached to the IUD. Using forceps, they will gently grasp the strings and then carefully pull the IUD out of the cervix. You may experience some mild cramping, but the procedure is generally well-tolerated and only takes a few minutes.
While IUDs are safe and effective birth control methods, some women have reported experiencing depression as a side effect. If you are experiencing persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness, talk to your healthcare provider about your concerns to determine the best course of action.
Is The Procedure Painful?
Removing an IUD typically does not cause significant pain, but you may experience some discomfort during the procedure.
Here’s what to expect during an IUD removal:
Your healthcare provider will use a speculum to open your vagina and locate the strings attached to the IUD.
They will use forceps to grasp the strings and gently tug on them to pull out the IUD. The procedure usually takes only a few minutes, and you may feel mild to moderate cramping or a pinching sensation during the removal.
If you experience extreme pain, fainting, or heavy bleeding, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Pro Tip: Discuss any concerns or questions you may have about the IUD removal procedure with your healthcare provider beforehand to ensure a comfortable and safe experience.
Possible Side Effects After Removal
IUD (Intrauterine Device) removal is a safe and uncomplicated procedure with minimal side effects. However, some women may experience mild to moderate symptoms after the removal process.
Potential side effects may include:
Cramping and discomfort: You may feel mild to moderate cramping and discomfort similar to menstrual cramps.
Spotting or bleeding: You may experience light bleeding or spotting for a few days after the removal.
Changes in menstrual cycle: Your menstrual cycle may be irregular for a few months following the removal.
Emotional changes: There is no evidence to support the claim that IUDs cause depression. However, some women associate their emotional changes with hormonal changes resulting from the use of IUD.
If you experience persistent and severe side effects after the removal of the IUD, you should contact your healthcare provider.
Pro Tip: To minimize discomfort during IUD removal, your healthcare provider may recommend taking a pain reliever such as ibuprofen before the procedure.
How to Choose The Right IUD
Considering an Intrauterine Device (IUD) as a form of contraception can feel like a big decision – and it is. There are different types of IUDs available, each with its own unique set of benefits and risks.
In addition to considering side effects like can iud cause depression, it’s important to understand the basics of how an IUD works, what types of IUDs are available, and how to choose the right one for you.
Factors To Consider Before Choosing An Iud
Before choosing an IUD, there are various factors that one should consider to ensure it fits their preferences, lifestyle, and medical history.
Type of IUD: There are two types of IUDs- hormonal and copper. Hormonal IUDs release small amounts of progestin to prevent pregnancy, while copper IUDs create a natural spermicide with their copper build. One must evaluate the pros and cons of both these types and consult a doctor to understand which is suitable for them.
Medical History: It is essential to consider existing medical conditions before picking an IUD. Anyone with a pre-existing hormonal condition or predisposition to certain cancers should consult with their doctor before opting for any hormonal IUDs.
Cost: Cost is another significant factor to consider before choosing an IUD. Copper IUDs last up to 10 years, while hormonal IUDs have an expiry date and may require more significant investment.
Mood Swings: While there is no clear evidence that IUDs can cause depression, hormonal IUDs could lead to mild mood changes in some people. One must discuss this with the physician beforehand.
Comfort: Ensuring the IUD is comfortable inside the body and does not cause any physical impairment is essential to see how it will hold up long-term.
Consulting your ob-gyn for personalized advice is crucial in deciding a suitable IUD.
The Pros And Cons Of Each Type Of IUD
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are a highly effective form of birth control that are safe and easy to use. However, like all contraceptives, there are pros and cons to each type of IUD that must be considered before making a decision.
Hormonal IUD: Pros – this type of IUD is highly effective, lasts up to six years, and can reduce menstrual bleeding and cramps. Cons – hormonal IUDs may cause hormonal side effects such as mood swings, acne, and headaches.
Copper IUD: Pros – this type of IUD is hormone-free, lasts up to 10 years, and is highly effective. Cons – Copper IUDs may increase menstrual bleeding and cramps, and in rare cases may cause expulsion or perforation of the uterus.
Ultimately, the decision of which type of IUD to use should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider based on individual health needs and preferences. It is important to note that while some studies suggest a link between hormonal contraception and depression, the majority of research shows no significant association.
Consultation With A Healthcare Provider
Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial when it comes to choosing the right IUD (Intrauterine Device) that works for you. An IUD is a form of birth control that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing an IUD:
Hormonal vs. Non-hormonal: Hormonal IUDs release progestin, which thickens the cervical mucus and prevents sperm from reaching the egg. Non-hormonal IUDs release copper, which is toxic to sperm.
Duration: Hormonal IUDs can last for up to 5 or 7 years, while non-hormonal IUDs can last for up to 10 years.
Side effects: Hormonal IUDs may cause hormonal side effects such as mood changes, headaches or weight gain. There is no evidence that IUDs cause depression. It is important to discuss any pre-existing medical conditions with a healthcare provider to determine which type of IUD works best for you.